Otoscopy: For the Hearing Healthcare Provider
# 1 in Otorhinolaryngology Textbooks :Amazon Canada
Otoscopy reveals the secrets of ear canal, ear drum, and middle ear. Performing this basic clinical procedure can be a challenge for the hearing instrument practitioners in the early years of their career. Familiarity with otoscopy and knowledge of the common conditions for which this procedure is performed is essential for hearing health care providers. The book explains the steps of the otoscopy procedure and discusses common findings in a simple and easy to understand manner. Colorful pictures of the normal and abnormal findings make grasping of the subject easy. Hearing Instrument Specialists (HIS) preparing for the International Licensing Examination (ILE) will find the book very useful as the pattern of questions asked in ILE has been kept in mind while preparing the material for various chapters of the book.
Buy Paperback or Kindle edition
Amazon USA: https://www.amazon.com/dp/B084Q9VS83
Amazon Canada: https://www.amazon.ca/dp/B084Q9VS83
Amazon UK: https://www.amazon.co.uk/dp/B084Q9VS83
Amazon Australia: https://www.amazon.com.au/dp/B084Q9VS83
Amazon India: https://www.amazon.in/dp/B08DCS93B1
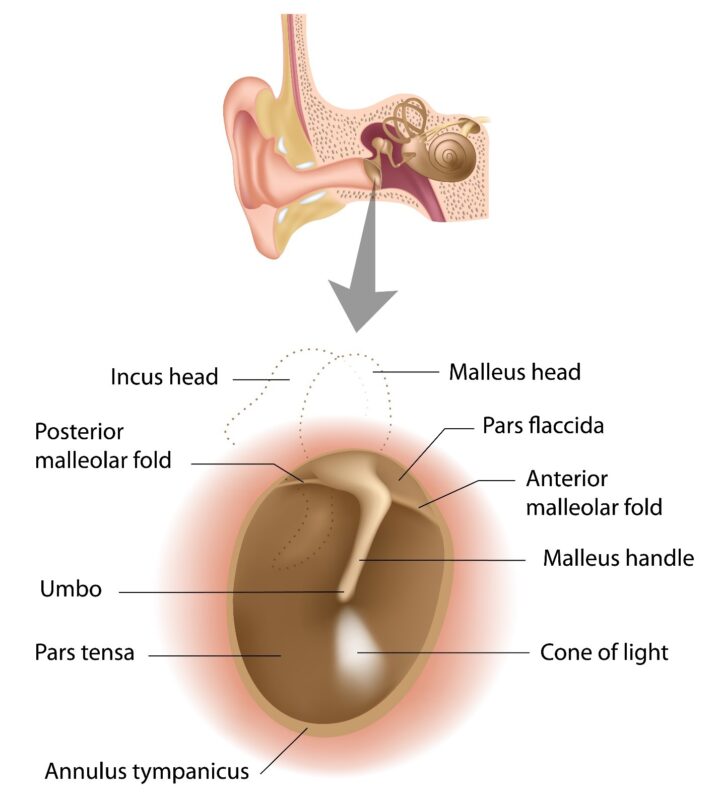
Figure 1: Right sided tympanic showing its landmarks
TM separates the middle ear from EAC. It is often referred to as ‘mirror of the middle ear cleft. TM is a three-layered structure; outermost layer is formed by keratinizing squamous epithelium which is continuous with skin of EAC. The middle layer is formed by fibrous tissue. This layer consists of an outer placed radially arranged fibers, inner layer of circular fibers, and third layer consists of parabolic fibers. These fibers together with a peripheral cartilaginous tympanic ring form the tympanic annulus. This annulus fits into tympanic sulcus, an incomplete ring formed mainly by the tympanic plate (a constituent of temporal bone). The third and inner most layer is mucosal, which is continuous with the mucosa of middle ear cleft (MEC). Because of this contiguity any inflammatory changes in MEC are reflected on to TM, hence the TM is called ‘mirror of the middle ear cleft’.
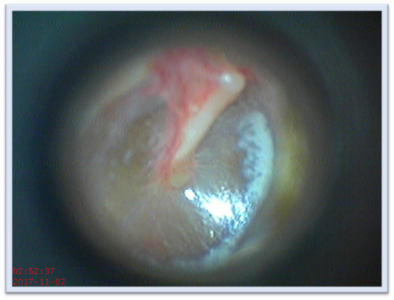
Figure 2: A video otoscopic view of right tympanic membrane
TM is an oval shaped, thin, pearly white to pinkish, which is concave laterally. Its dimensions are 9-10 mm in length, 8-9 mm in width, and 0.1 mm in thickness. In an adult it is placed slanting and forms an angle of approximately 550 with the floor, thus floor of EAC is longer than its roof. TM is also forward facing making anterior wall of EAC longer than its posterior wall.
Of the three middle ear ossicles, the handle of malleus (HOM) lies in between skin and fibrous layers. It is directed downwards, backwards, and medially. HOM provides a medial pull, which is maximum near the center of pars-tensa, this point of maximum concavity is called umbo. The peripherally placed tympanic annulus converges towards malleus to attach with its neck to form anterior and posterior malleolar folds. These folds divide the TM into two parts, lower pars tensa and upper pars flaccida. Pars tensa is sturdier of the two because of the presence of fibrous layer and is pearly-white in color. Pars flaccida is devoid of fibrous element it is pinkish in color and delicate in strength. Once you can visualize the TM, move it all around to look at various landmarks of TM.
On otoscopy (See figure 2) TM appears as an oval shaped, pale colored, semi-transparent, glistening structure which is held taut by the handle of malleus. Following landmarks can be seen on a normal TM (See figure1):
- Handle of Malleus, which is directed downwards, backwards, and slightly inwards.
- Umbo, the point of maximum concavity of TM.
- The anterior and posterior malleolar folds which are attached to lateral process of malleus & divide TM into two parts pars-tensa (below) and pars-flaccida (above).
- Lateral process of Malleus.
- The cone of light, which is always placed in antero-inferior quadrant of pars- tensa (at 5 O’clock in right and at 7 O’clock in left TM)
As one gradually gains experience and confidence you can attach a pneumatic bulb to the otoscope to do pneumatic otoscopy to check the mobility of TM.
Buy the paperback and Kindle editions:
Amazon USA:
https://www.amazon.com/dp/B084Q9VS83Amazon Canada:
https://www.amazon.ca/dp/B084Q9VS83Amazon UK:
https://www.amazon.co.uk/dp/B084Q9VS83Amazon Australia:
https://www.amazon.com.au/dp/B084Q9VS83Amazon India:
https://www.amazon.in/dp/B08DCS93B1